HTML
HTML is a computer language devised to allow website creation. These websites can then be viewed by anyone else connected to the Internet. It is relatively easy to learn, with the basics being accessible to most people in one sitting;
The definition of HTML is HyperText Markup Language.
HyperText is the method by which you move around on the web — by clicking on special text called hyperlinks which bring you to the next page. The fact that it is hyper just means it is not linear — i.e. you can go to any place on the Internet whenever you want by clicking on links — there is no set order to do things in.Markup is what HTML tags do to the text inside them. They mark it as a certain type of text (italicised text, for example).HTML is a Language, as it has code-words and syntax like any other language.
A Simple HTML Document
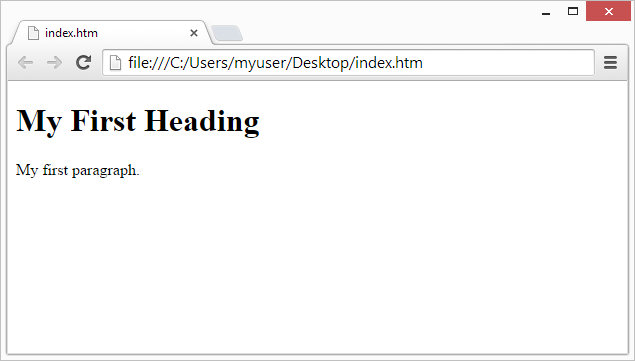
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Example Explained
The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines this document to be HTML5The <html> element is the root element of an HTML pageThe <head> element contains meta information about the documentThe <title> element specifies a title for the documentThe <body> element contains the visible page contentThe <h1> element defines a large headingThe <p> element defines a paragraph
HTML Tags
HTML tags are element names surrounded by angle brackets:
<tagname>content goes here...</tagname>
HTML tags normally come in pairs like <p> and </p>The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tagThe end tag is written like the start tag, but with a forward slash inserted before the tag name
Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, IE, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them.
The browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
HTML Page Structure
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:


Comments
Post a Comment